The Future of Visuals: The Emergence of Synthetic Images
Unleashing the Boundless Potential of Digital Imagination
Synthetic images are created using computer graphics software (e.g., 3D modelling, computer animation, and photorealistic rendering) rather than the traditional photographic technique of focusing light waves with cameras or other optical devices. These graphics are used in a variety of fields, including video games, movies, advertising, and architectural visualisation.
They have grown in popularity in recent years as a result of technological improvements and an increase in demand for high-quality graphics in the entertainment sector that are supposed to replicate real-world situations and objects.
The data is derived from sensors that detect information that is unseen to the human eye, and the pictures are then produced for visualisation or more Machine Learning (ML) processing to extract information and objects from the scene. The core advantage of Synthetic Imaging, when combined with appropriate geospatial technologies and professional services, is the ability of Image Analysts (IA), their supervisors, and other interested parties to visually understand specified surfaces, textures, shapes, patterns, movements, and more that could never be seen in "real" images, such as photos.
Advantages of Synthetic Images
They are quick and simple to make. This is especially effective in sectors like architecture and product design, where several iterations of a design can be developed and reviewed quickly.
They may be used to simulate real-world circumstances that are difficult or impossible to reproduce in a physical context. Synthetic pictures can be used to mimic the influence of weather conditions on a building or to investigate the behaviour of a fluid in a complicated environment.
They may be produced with great precision and control. This enables the generation of realistic graphics capable of simulating real-world circumstances.
For example, synthetic images produce realistic architectural representations of yet-to-be-built structures. Architects, developers, and builders may use these images to see the finished result and make any required modifications before work begins.
In the entertainment sector, synthetic images are utilised to generate realistic special effects for movies and video games. Computer-generated characters and settings are extremely realistic, making it difficult to tell them apart from their real-world counterparts. This enables the development of fanciful worlds and characters that would be hard to achieve using live-action videos.
Medical researchers use synthetic images to generate realistic models of the human body that are used to investigate disorders and develop novel remedies.
In the advertising business, synthetic images are utilised to produce extremely realistic and interesting product representations for use in print and web commercials. This enables the production of extremely engaging commercials that are used to display things in ways that traditional photography cannot.
4)They can be tweaked and modified in ways that traditional photography does not allow. For example, synthetic images are created with varying lighting, camera angles, and weather conditions. This enables creators to build a diverse set of graphics that may be utilised in various areas of a game or movie.
Methods of Creating Synthetic Images
The earliest synthetic images were generated in the late 1950s and early 1960s when computer scientists began to experiment with utilising computers to make images. The first synthetic images were simply geometric forms and lines, but as technology advanced, the images got more intricate and lifelike.
The debut of raster graphics and the development of computer animation software in the 1970s and 1980s signified a large leap in the possibilities of synthetic images. This enabled the creation of more realistic images and animation, paving the way for the creation of early computer-generated films and video games.
The introduction of 3D computer graphics and the development of sophisticated rendering software in the 1990s resulted in a considerable rise in the realism and complexity of synthetic images. This enabled the fabrication of lifelike visuals and animation, which paved the way for the development of increasingly complex computer-generated films and video games.
Types of Synthetic Images
There are various varieties of synthetic images, each with its own set of qualities and applications.
2D Synthetic Images
2D synthetic images are computer-generated images that are intended to resemble two-dimensional real-world situations and objects. They're usually made with 2D graphics tools like Adobe Photoshop or Illustrator. 2D synthetic pictures are often utilised in digital art, web design, and advertising.
3D Synthetic Images
Computer-generated images in three dimensions that resemble real-world objects and scenes are known as 3D synthetic images. Typically, 3D graphics programmes like Autodesk Maya or Blender are used to make them. In the production of computer-generated movies and video games, as well as in architectural visualisation and product design, 3D synthetic images are often employed.
Real-time synthetic images
Real-time synthetic images are designed by computers and intended to be rendered in real-time, or more precisely, at the same rate as user interaction. Usually, gaming engines like Unity or Unreal Engine are used to develop them. Virtual reality, augmented reality, and video games all frequently use real-time synthetic images.
Methods for Producing Synthetic Images
Synthetic images may be produced using a variety of techniques.
1. Raster Graphics
The most popular kind of synthetic image is raster graphics. They are composed of pixels, which are very little colour dots that make up an image. Applications for raster graphics include video games, marketing, and web design.
Vector Graphics
To describe the shapes and lines of an image, mathematical procedures are used to produce vector graphics. Vector graphics may be enlarged without losing quality, unlike raster graphics, which cannot. Illustrations, animations, and logos frequently use vector graphics.
3D Modeling
Making a 3D representation of an object or scene is called 3D modelling. Images and animations can then be produced using this representation. Animation, product design, and architecture are three fields that frequently use 3D modelling.
Procedural Generation
The term "procedural generation" describes the process of producing graphics using algorithms. The algorithms may be used to create intricate patterns, textures, and forms. Video games and virtual worlds use procedural generation.
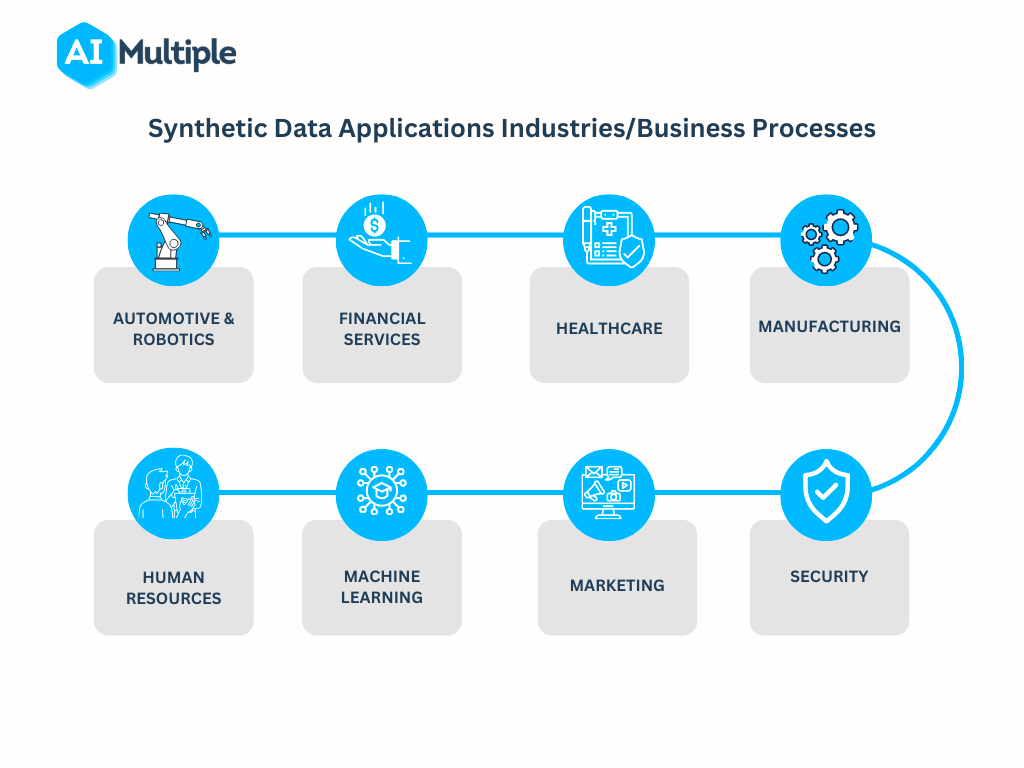
Applications of Synthetic Images
Advertising
Advertising frequently uses fake imagery. Images that are impossible to capture in real life are produced using them. For instance, the creation of images of items that haven't yet been released can be done using synthetic images.
Gaming
Synthetic images have been used in video games for decades. Technology advancements have led to an increase in the realism of video games, and synthetic visuals have been a major factor in this. Characters, settings, and special effects in video games are all created using synthetic imagery.
Animation
Synthetic images have been used in animation since the early days of computer graphics. Characters and settings in animations are made using synthetic images. Animations today appear more realistic because of the development of 3D computer graphics and are employed in a variety of fields, such as cinema, television, and advertising.
Medical Imaging
The use of synthetic images in medicine is known as medical imaging. Images of the human body may be produced using medical imaging techniques including:
X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs. Additionally, 3D models of organs and tissues may be made using synthetic images, and these models can be utilised for surgical planning and simulation.
Computer-generated Films and Video Games
Synthetic images are used in computer-generated movies and video games to provide lifelike and animated settings and characters. This makes it possible to create experiences that are more immersive and lifelike, as well as scenarios and people that would be hard to produce in real life.
Architectural Visualization
Photorealistic representations of architectural projects are produced using synthetic images in architectural visualisation. This enables architects and designers to create realistic, detailed visualisations of their plans and to make modifications and alterations before the structure is ever built.
Product Design
Photorealistic representations of product designs are made using synthetic images. This makes it possible for designers and manufacturers to view their concepts in a precise and realistic manner and to make adjustments before the product is produced.
Challenges and Limitations of Synthetic Images
A synthetic image, however, is not genuine, and it is challenging to accurately simulate the behaviour of real-world objects and environments. This could be a drawback in disciplines like engineering and science, where the aim is to accurately model a system in the actual world.
Future of Synthetic Images
In general, synthetic images are a useful tool for a variety of uses, from design and entertainment to science and engineering. Synthetic images are a useful and effective tool for many different disciplines due to their capacity to produce high-quality photographs fast and simply as well as to replicate real-world settings.
The use of machine learning in synthetic images comes last. The process of teaching computers to learn from data is known as machine learning. Developers may produce synthetic visuals that are incredibly lifelike and resemble the actual world by applying machine learning.
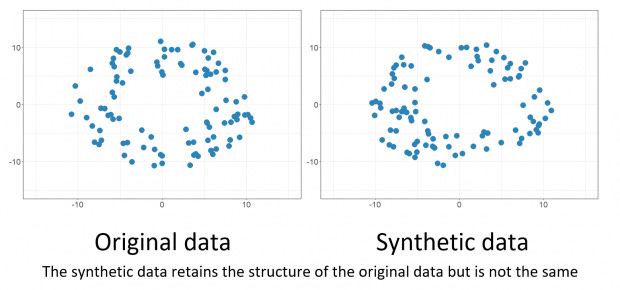
Researchers have recently been able to produce synthetic images that are more and more realistic and that can be used to train machine learning models thanks to the advancement of artificial intelligence, generative models, and deep learning. Examples of this include Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and Variational Autoencoders (VAEs). These models may produce new, synthetic images that are similar to the ones in the training set by first being trained on enormous datasets of real-world photos.
Conclusion: The Importance of Synthetic Images in Today's World.
Synthetic images have become an integral part of modern technology and are used in various fields, including advertising, gaming, animation, and medical imaging. With advancements in technology, synthetic images have become increasingly realistic, and their applications are only limited by our imagination. Synthetic images have opened up new avenues for creativity and innovation, and the future of synthetic images looks bright.
Synthetic images have become increasingly popular in recent years due to advancements in technology and the increasing demand for high-quality visuals in the entertainment industry. With the increasing demand for high-quality visuals, synthetic images will continue to play a major role in the entertainment industry and other fields.
This article was originally published on the company blog.
Intellicy is a consultancy firm specialising in artificial intelligence solutions for organisations seeking to unlock the full potential of their data. They provide a full suite of services, from data engineering and AI consulting to comment moderation and sentiment analysis. Intellicy's team of experts work closely with clients to identify and measure key performance indicators (KPIs) that matter most to their business, ensuring that their solutions generate tangible results. They offer cross-industry expertise and an agile delivery framework that enables them to deliver results quickly and efficiently, often in weeks rather than months. Ultimately, Intellicy helps large enterprises transform their data operations and drive business growth through artificial intelligence and machine learning.