Boost Efficiency and Slash Workload for Your Business Processes with Robotic Process Automation
Transform Your Operations with Robotic Process Automation: Benefits, Challenges, and Best Practices for Implementation
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is a type of automation technology that allows companies to automate repetitive and manual tasks that were previously performed by humans. RPA uses artificial intelligence and machine learning capabilities to perform tasks that require decision-making, such as data extraction, data processing, and data entry.
You can think of RPA as a software robot or virtual assistant that can perform tasks such as data entry, data extraction, invoice processing, report generation, and customer support.
RPA can be seen as a precursor to artificial intelligence and machine learning because it relies on predefined rules and logic to automate tasks, while artificial intelligence and machine learning can learn from data and improve over time.
RPA is becoming increasingly popular in many industries because it can improve the efficiency, accuracy, and speed of business processes. Implementing RPA can present technical, organisational, security, and compliance challenges. Organisations should set clear goals and expectations, select the right processes for automation, engage key stakeholders, and provide appropriate training and support to ensure successful implementation.
How does It work?
The process of RPA typically involves identifying the tasks that can be automated, designing the workflow, and creating the automation scripts. RPA is different from traditional automation in that it can work on a wide range of tasks and applications without requiring significant changes to the underlying systems.
RPA is composed of three components: the robot, the control panel, and the processing layer.
The robot is the software that performs the tasks
The control panel is the interface that allows users to configure and monitor the robot, and
The processing layer is the system that receives and processes the data.
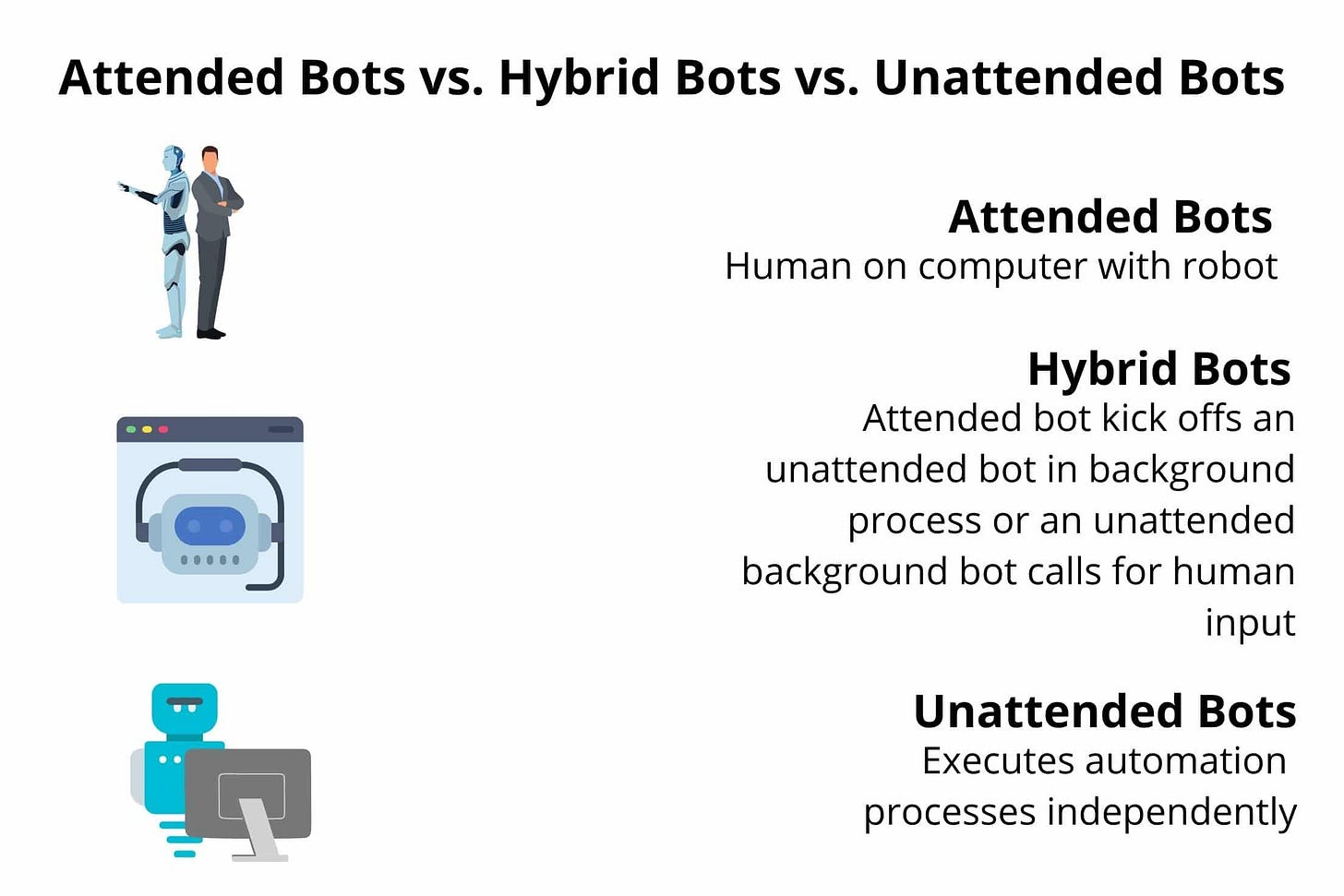
RPA bots, or just 'bots', are software programs that you set up to do digital work. They're often called a Digital Workforce. RPA bots can interact with any system or application the same way you do. It's as simple as showing your bots what to do, then letting them do the work. They work by following pre-defined rules and logic that are programmed by humans. RPA bots can interact with different types of systems such as web applications, desktop applications, mainframes, and databases. RPA bots can also communicate with humans through chatbots or voice assistants.
RPA bots can be programmed to perform tasks in different ways, such as:
Rule-based automation: RPA bots can follow a set of rules and logic to perform tasks. For example, an RPA bot can be programmed to extract data from a PDF document and input it into an Excel spreadsheet.
Screen scraping: RPA bots can extract data from a user interface by capturing images of screens and analyzing them. For example, an RPA bot can extract data from a web page by capturing images of tables and text fields and extracting the relevant data.
Workflow automation: RPA bots can automate end-to-end business processes by integrating with different systems and applications. For example, an RPA bot can automate the process of invoice processing by extracting data from emails, inputting it into a database, and sending notifications to stakeholders.
Benefits of RPA
RPA offers several benefits to organisations, such as:
Cost savings: RPA can help organisations reduce costs by automating routine and repetitive tasks that were previously done by humans. RPA can also help organisations reduce errors and improve productivity, which can lead to cost savings in the long run.
Accuracy: RPA bots can perform tasks with a high degree of accuracy and consistency, which can reduce errors and improve the quality of work.
Efficiency: RPA bots can perform tasks much faster than humans, which can lead to faster turnaround times and improved customer satisfaction.
Scalability: RPA bots can be scaled up or down based on the needs of the organisation. RPA can also be used to automate multiple tasks and processes across different departments, which can lead to greater scalability and flexibility.
Compliance: RPA can help organisations ensure compliance with regulatory requirements by automating tasks that require strict adherence to rules and regulations.
By automating manual tasks, organisations can reduce errors and increase productivity, allowing employees to focus on more strategic tasks.
Use Cases
RPA is being used across a wide range of industries, including financial services, healthcare, manufacturing, human resources, and customer service. In financial services, RPA is being used for tasks such as accounts payable and accounts receivable, while in healthcare, it is being used for tasks such as claims processing and medical records management.
Challenges of Implementing
Implementing Robotic Process Automation (RPA) can present several challenges to organisations. These challenges can be classified into technical, organisational, security, and compliance challenges.
Technical challenges arise from the complexity of automated systems and the integration of RPA with existing systems. Organisations must ensure that the systems and processes being automated are suitable for automation and that the automation is aligned with the organisation's goals and objectives. In some cases, organisations may need to modify their existing systems to enable RPA to work effectively. In addition, organisations must ensure that the RPA bots are reliable, scalable, and easy to maintain.
Organisational challenges arise from the need to change the way work is done, and the way employees interact with technology. RPA can lead to a significant shift in the roles and responsibilities of employees, and organisations must ensure that they have the right skills and resources to manage this transition. In addition, organisations must ensure that employees are trained to use RPA effectively and that they understand the benefits and limitations of the technology.
Security and compliance challenges arise from the need to ensure that RPA does not compromise the security and privacy of sensitive data. Organisations must ensure that RPA bots are secure and that they comply with regulatory requirements such as data protection laws and industry standards. In addition, organisations must ensure that they have the right governance and oversight mechanisms in place to monitor and manage the use of RPA.
To ensure the successful implementation of RPA, organisations should establish clear goals and expectations, select the right processes for automation, engage key stakeholders, and provide proper training and support. Continuous monitoring and improvement are also essential for maintaining the effectiveness of RPA.
Best Practices for Implementing
The following are some best practices for implementing RPA:
Establish clear goals and expectations: Organisations should establish clear goals and expectations for implementing RPA. This includes identifying the processes that can be automated, defining the outcomes that the organisation wants to achieve, and setting realistic timelines and budgets.
Select the right processes for automation: Organisations should select the processes that are suitable for automation. This includes repetitive processes and rule-based processes that require minimal human intervention. Organisations should also consider the complexity of the processes and the potential benefits of automation.
Engage key stakeholders: Organisations should engage key stakeholders in the implementation of RPA. This includes employees who will be affected by the automation, such as those who perform the tasks being automated. Engaging key stakeholders can help organisations identify potential issues and risks and address them proactively.
Ensure proper training and support: Organisations should ensure that employees are trained to use RPA effectively and that they understand the benefits and limitations of the technology. Proper training and support can help employees adapt to the changes brought about by automation and use RPA effectively.
Continuous monitoring and improvement: Organisations should continuously monitor the effectiveness of RPA and make improvements as necessary. This includes monitoring the performance of the RPA bots, identifying and resolving issues and errors, and optimizing the processes being automated.
By following these best practices, organisations can ensure the successful implementation of RPA and reap the benefits of automation, such as cost savings, increased efficiency and accuracy, improved compliance and audibility, and enhanced customer experience.
However, organisations must also ensure that the automation aligns with their goals and objectives and that they comply with regulatory requirements and ethical considerations. By addressing these challenges and following best practices, organisations can realize the full potential of RPA and stay ahead of the competition.
Future of RPA
The future of RPA looks promising, with emerging trends and technologies such as cognitive automation and chatbots.
It is a rapidly growing technology that is transforming the way businesses operate. RPA has already proven to be an effective tool for automating repetitive and manual tasks, reducing costs, and improving efficiency. However, the future of RPA looks even more promising, with emerging trends and technologies that are expected to drive further growth and innovation in this field.
The most promising trends in the future of RPA are:
1. The development of cognitive automation: Cognitive automation combines RPA with artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) technologies to enable bots to perform more complex tasks that require decision-making and problem-solving skills. Cognitive automation can be used to automate tasks such as customer service, fraud detection, and supply chain management, which require a higher cognitive ability than traditional RPA.
2. The use of chatbots and virtual assistants: Chatbots and virtual assistants are AI-powered tools that can interact with humans through natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning algorithms. Chatbots and virtual assistants can be used to automate tasks such as customer support, sales, and marketing, and can provide a more personalized and efficient experience for customers.
3. The integration of RPA with other emerging technologies such as blockchain, the Internet of Things (IoT), and cloud computing. RPA can be used to automate tasks such as data entry, processing, and analysis in blockchain-based systems, IoT devices, and cloud platforms. This integration can lead to greater efficiency, scalability, and security in these systems.
However, the future of RPA also presents some challenges and ethical considerations that must be addressed.
The potential impact on the workforce: RPA can automate many routine and repetitive tasks, which can lead to job displacement and a shift in the roles and responsibilities of employees. Organisations must ensure that they have the right skills and resources to manage this transition and that they provide adequate training and support to employees.
The potential for bias and discrimination in decision-making: RPA bots can be programmed with biases that reflect the biases of their creators, which can lead to unfair and discriminatory decisions. Organisations must ensure that they have the right governance and oversight mechanisms to monitor and manage the use of RPA and that it aligns with ethical and social considerations.
Conclusion
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is a valuable technology that has gained significant attention in recent years because it enables organisations to automate routine and repetitive tasks that were previously performed by humans. It is being used across a wide range of industries, including financial services, healthcare, manufacturing, human resources, and customer service. The importance of RPA for organisations lies in its ability to transform the way businesses operate. By automating routine and repetitive tasks, RPA can help organisations increase efficiency, reduce costs, and improve the quality of work.
In addition to its benefits, RPA does present some challenges, such as technical, organisational, security, and compliance concerns. To ensure the successful implementation of RPA, organisations must address these challenges by establishing clear goals and expectations, selecting the right processes for automation, engaging key stakeholders, and providing proper training and support. Continuous monitoring and improvement are also essential for maintaining the effectiveness of RPA.
In conclusion, RPA is a valuable technology that can benefit organisations significantly. The future looks promising, with emerging trends and technologies. However, organisations must address the challenges and ethical considerations associated with RPA to ensure that it aligns with their goals and objectives and that it benefits society as a whole. RPA can also help organisations stay competitive in a rapidly changing business environment by enabling them to adapt quickly to new challenges and opportunities.
This article was originally published on a company weblog. you can read the original one here.
Intellicy is a consultancy firm specialising in artificial intelligence solutions for organisations seeking to unlock the full potential of their data. They provide a full suite of services, from data engineering and AI consulting to comment moderation and sentiment analysis. Intellicy’s team of experts work closely with clients to identify and measure key performance indicators (KPIs) that matter most to their business, ensuring that their solutions generate tangible results. They offer cross-industry expertise and an agile delivery framework that enables them to deliver results quickly and efficiently, often in weeks rather than months. Ultimately, Intellicy helps large enterprises transform their data operations and drive business growth through artificial intelligence and machine learning.